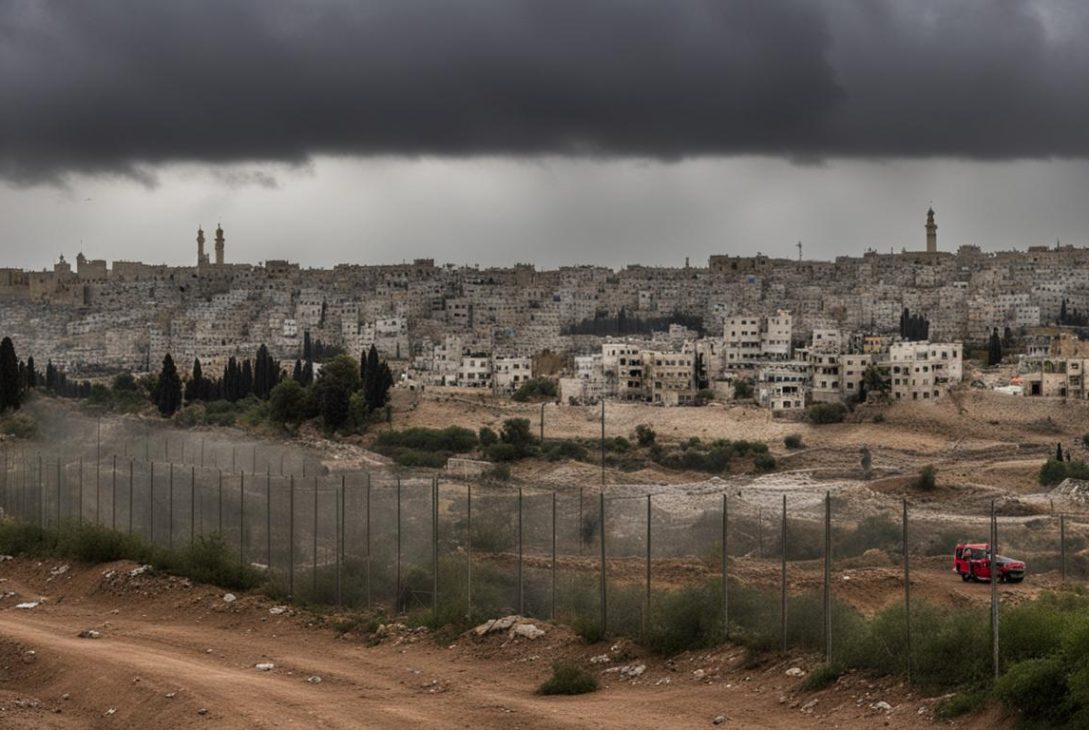
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, one of the bloodiest and longest-running conflicts in modern history, has caused immense suffering and loss of life for over 75 years. In search of lasting peace, the two-state solution has been proposed as a potential pathway towards resolving this entrenched conflict. This solution entails the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, aiming to address the aspirations and rights of both parties involved. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of the two-state solution, its historical origins, the challenges it faces, and its potential to bring about peace in the Middle East.
Key Takeaways:
- The two-state solution is a proposed framework for resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- It involves the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel.
- The origins of this solution can be traced back to the United Nations’ partition plan in 1947.
- Negotiating borders and addressing Israeli settlements remain significant challenges.
- There are alternative perspectives, such as advocating for equal rights for all individuals in the region.
The Origins of the Two-State Solution
The origins of the two-state solution can be traced back to the partition plan proposed by the United Nations in 1947. The plan aimed to divide Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, providing a potential solution to the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. However, while the Jewish community embraced this plan as a legal justification for the establishment of Israel, the Arab community rejected it, leading to ongoing tensions and conflicts.
The question of land sharing between Israel and a future Palestinian state remains a central issue in the two-state solution. The establishment of Israeli settlements in the occupied Palestinian territories has further complicated the situation, as it has raised disputes over land ownership and hindered progress towards a lasting peace agreement. The presence of these settlements has been a major obstacle in negotiations and has created tension between the two sides.
| Israeli Settlements | Palestinian Statehood |
|---|---|
| The construction of Israeli settlements in the occupied territories has hindered progress towards a two-state solution. | Palestinians view the establishment of a sovereign state as their right and a key component of any potential peace agreement. |
| The expansion of settlements has raised disputes over land ownership and complicated negotiations. | The question of Palestinian statehood remains a central issue in the two-state solution. |
| Settlements violate international law and contribute to the fragmentation of Palestinian territory. | Recognition of Palestinian statehood by the international community is crucial for the two-state solution. |
The complexities surrounding land sharing and Palestinian statehood continue to shape the two-state solution. Achieving a just and enduring resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict requires addressing these issues and finding a mutually agreed framework for the establishment of two separate and viable states.
Challenges and Obstacles
Implementing the two-state solution has proven to be challenging due to various obstacles. Negotiating borders between Israel and a future Palestinian state has been a significant point of contention. The Israeli settlements in the occupied Palestinian territories have also been a major obstacle, leading to disputes over land ownership and creating tension between the two sides. These challenges have hindered progress towards a lasting peace agreement.
Border Negotiation Challenges
Border negotiation is a critical aspect of the two-state solution, as it determines the physical boundaries between Israel and a future Palestinian state. Both parties have differing perspectives on where the borders should be drawn, with each side seeking to secure their strategic interests and ensure the viability of their respective states. This intricate process involves addressing complex issues such as the status of Jerusalem, the division of land resources, and the establishment of secure borders. The border negotiation challenges have resulted in protracted discussions and an ongoing stalemate, contributing to the difficulties in implementing the two-state solution.
Israeli Settlements and Land Ownership Disputes
The presence of Israeli settlements in the occupied Palestinian territories remains a significant obstacle to the two-state solution. These settlements are regarded as illegal under international law and have been a source of contention between Israel and the Palestinians. The establishment and expansion of these settlements, which house Israeli civilians in the West Bank and East Jerusalem, have resulted in the displacement and dispossession of Palestinians from their lands. This has created deep-seated grievances, fueling tensions and making it challenging to reach a mutually acceptable agreement on land ownership and territorial sovereignty.
“The presence of Israeli settlements in the occupied territories is a major obstacle to peace. It undermines the prospects for a two-state solution and contravenes international law.” – United Nations
The Way Forward
To overcome these challenges and achieve progress towards the two-state solution, it is crucial for both parties to engage in meaningful dialogue and negotiations. The international community, including key stakeholders such as the United Nations and the United States, can play a crucial role in facilitating and mediating these discussions. It is essential to address the core issues of border negotiation and Israeli settlements, finding mutually agreed-upon solutions that uphold the rights and aspirations of both Israelis and Palestinians. By overcoming these obstacles, a pathway to peace can be forged, where both nations can coexist side by side within recognized and secure borders.
Alternatives to the Two-State Solution
Some experts argue that the two-state solution is no longer feasible and that the current reality on the ground resembles a one-state apartheid situation. They suggest that shifting the focus towards advocating for equal rights for all, regardless of nationality, could be a more viable alternative. This approach would involve Palestinians demanding their rights and working towards a future where everyone has equal rights, rather than pursuing a separate Palestinian state.
“The idea of a two-state solution is increasingly seen as unrealistic in light of the ongoing Israeli settlements and the lack of progress in negotiations. The current situation resembles a one-state apartheid system where Palestinians are subject to discriminatory policies and limited rights,” says Dr. Rachel Abbas, a Middle East expert.
Supporters of this alternative argue that it would address the fundamental issue of equal rights and ensure a more just and inclusive society. They argue that a shared, democratic state guarantees equal representation and protection of the rights of both Israelis and Palestinians.
Comparative Analysis of the Two-State Solution and the Equal Rights Approach
| Two-State Solution | Equal Rights Approach | |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Erect separate Israeli and Palestinian states | Advocate for equal rights and a shared, democratic state |
| Implementation | Negotiations and agreements between Israeli and Palestinian leadership | Grassroots movements and international pressure |
| Land Ownership | Reconsider distribution and divisions of land | Ensure equal land rights for Israelis and Palestinians |
| Security | Create separate security forces for Israeli and Palestinian territories | Establish joint security forces to ensure the safety of all citizens |
| International Support | Requires diplomatic efforts to gain international recognition and support | Depends on international pressure and advocacy |
| Challenges | Border negotiations, settlements, and refugee repatriation | Overcoming historical animosities and mistrust |
While the concept of equal rights has gained traction among some activists and scholars, critics argue that it fails to address practical concerns and ignores the complexities of the conflict. They argue that a one-state solution would disrupt the delicate demographic balance and potentially lead to further violence and unrest. Critics also point out that achieving equal rights for all would require significant changes to the current political and social landscape, necessitating a monumental shift in attitudes and policies.
Despite the challenges, the alternative approach of advocating for equal rights continues to be a topic of discussion and debate in the context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It represents a departure from the traditional two-state solution and opens up new possibilities for envisioning a future where Israelis and Palestinians coexist as equal citizens within the same state.
The Role of Youth

The youth of today play a significant role in shaping the outcome of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. As the next generation, their perspectives, energy, and actions have the potential to create meaningful change. This emerging youth movement is characterized by a growing shift in public opinion, particularly in the United States, towards supporting Palestinians and being critical of Israeli policies.
The voices of the young are instrumental in challenging the status quo and advocating for a more just and equitable solution to the conflict. They bring fresh ideas and a renewed sense of urgency to the table, pushing for alternative approaches and highlighting the importance of human rights and social justice.
By leveraging their influence through social media, grassroots activism, and engagement in political discourse, the youth have the power to shape public opinion, impact policy decisions, and ultimately contribute to the resolution of the conflict. Their involvement is crucial in ensuring that the perspectives of future generations are represented and that the outcome of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict aligns with their aspirations for peace and coexistence.
Perspectives on Solving the Conflict
When it comes to finding a resolution for the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, there are differing perspectives on the most effective approach. Some advocate for a top-down approach, focusing on peace agreements signed at the highest levels of leadership. This strategy emphasizes diplomatic negotiations between Israeli and Palestinian leaders, with the belief that a comprehensive agreement can address the complex issues at hand. Proponents argue that this approach can lead to a more stable and lasting solution.
On the other hand, there are those who believe in a bottom-up approach, which emphasizes grassroots movements and individual actions. This perspective recognizes the importance of engaging local communities, civil society organizations, and individuals in promoting peace and reconciliation. By fostering dialogue, building trust, and addressing the needs and grievances of both Israelis and Palestinians, this approach aims to lay the foundation for a sustainable resolution. It recognizes that peace is not only a matter for political leaders but also a collective effort.
It is important to note that both the top-down and bottom-up approaches have their strengths and limitations. The top-down approach can lead to significant progress in negotiations and address larger political and security issues. However, it may overlook the grassroots realities and the perspectives of the people directly affected by the conflict. Conversely, the bottom-up approach brings local voices to the forefront and promotes inclusivity. Yet, it may face challenges in achieving widespread consensus and addressing broader structural issues.
Ultimately, many experts argue that a combination of these approaches is necessary for a comprehensive and sustainable resolution. Diplomatic efforts at the top level can provide the framework and political will for peace, while grassroots advocacy and engagement can foster an environment conducive to reconciliation and cooperation. By recognizing the importance of both approaches, the international community can support a multi-faceted approach that takes into account the needs and aspirations of all parties involved.
Looking Ahead
The future of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains uncertain. The ongoing tensions and complexities surrounding the two-state solution make it challenging to predict the outcome. However, several factors may shape the future direction of the conflict.
Firstly, the international community’s involvement and commitment to finding a peaceful resolution will play a crucial role. Countries supporting the two-state solution and investing in the Palestinian economy can contribute to building trust and stability in the region. Efforts to promote dialogue, negotiation, and diplomacy will continue to be vital in order to achieve a lasting peace agreement.
Secondly, the perspective and actions of the younger generation will have a significant impact on the conflict’s outcome. The emerging youth, both in Israel and Palestine, bring new ideas, perspectives, and energy to the table. Their ability to challenge existing narratives, advocate for peace, and engage in grassroots movements can shape the path towards a more peaceful future.
| Efforts | Description |
|---|---|
| Support for the Two-State Solution | Many countries, including Australia, actively support the two-state solution as the preferred framework for achieving lasting peace. Their diplomatic efforts aim to reinforce the importance of a durable peace agreement. |
| International Investment | Investments in the Palestinian economy can help improve living conditions, create job opportunities, and enhance socio-economic stability. This, in turn, can foster an environment conducive to peace. |
| Settlements Violation | International pressure to end Israeli settlement expansion in the occupied territories is crucial in order to create an environment conducive to meaningful negotiations and the establishment of a Palestinian state. |
“The future of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict depends on the collective efforts of the international community, the younger generation, and a commitment to the two-state solution. It requires a shift in perspectives, a focus on human rights and coexistence, and a dedication to finding common ground.”
While the road ahead may be challenging, achieving a just and enduring solution remains a shared goal. The future of the conflict will be determined by the willingness of both sides to engage in meaningful dialogue, address key issues such as borders and settlements, and work towards a future of peace, security, and prosperity.
International Efforts for Peace
The international community plays a crucial role in advocating for a peaceful resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Many countries, including Australia, support the two-state solution as the preferred framework for achieving lasting peace. They call for an end to Israeli settlement expansion, the dismantling of Hamas, and serious investment in the Palestinian economy. International diplomatic efforts aim to reinforce the imperative of a durable peace and ensure that all parties involved respect the rights and existence of the other.
In order to support the two-state solution, international investment in the region is crucial. Financial support can help improve the Palestinian economy, create jobs, and provide opportunities for growth and development. By investing in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, the international community can contribute to building the necessary foundations for a future Palestinian state. This investment not only benefits the Palestinian people but also contributes to the overall stability and prosperity of the region.
| Two-State Solution Support | International Investment | Settlements Violation |
|---|---|---|
| ⟨Country 1⟩ | ⟨Amount⟩ | ⟨Number of Violations⟩ |
| ⟨Country 2⟩ | ⟨Amount⟩ | ⟨Number of Violations⟩ |
| ⟨Country 3⟩ | ⟨Amount⟩ | ⟨Number of Violations⟩ |
The table above showcases the support for the two-state solution, international investment, and the violations of settlements by different countries. It presents a clear visual representation of the varying levels of commitment and involvement from the international community. By addressing the issue of settlements and investing in the Palestinian economy, the international community can contribute significantly to the realization of a two-state solution and a lasting peace in the region.
Conclusion
The two-state solution stands as a potential pathway to peace in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, amidst ongoing debates and challenges. Despite the obstacles faced, there remains hope for a just and enduring resolution. The involvement of emerging young voices, international support, and a commitment to human rights and coexistence are crucial in shaping a better future for both Israelis and Palestinians.
To achieve lasting peace, it is essential to prioritize the voices of the youth who hold the power to influence policy decisions and reshape the conflict’s trajectory. Furthermore, international support plays a vital role, with many countries advocating for the two-state solution and emphasizing the need to address issues such as Israeli settlement expansion and Palestinian economic development.
While the road ahead may be difficult, the ultimate goal should be a peaceful coexistence where Israelis and Palestinians can live securely and prosperously within internationally recognized borders. The future prospects for the Israeli-Palestinian conflict depend on the commitment to a pathway to peace, with a focus on diplomacy, dialogue, and respect for the rights and existence of both parties.
FAQ
What is the two-state solution?
The two-state solution refers to the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel as a potential pathway to peace in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
When was the two-state solution proposed?
The United Nations proposed the two-state solution in 1947 as part of a partition plan to divide Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states.
What are the challenges of implementing the two-state solution?
Negotiating borders and addressing Israeli settlements have been significant obstacles in implementing the two-state solution.
Are there alternatives to the two-state solution?
Some suggest advocating for equal rights for all, regardless of nationality, as an alternative approach to addressing the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
What role do young people play in the conflict?
The youth have the power to shape the future outcome of the conflict through their perspectives and influence on policy decisions.
What are the different perspectives on solving the conflict?
Some argue for a top-down approach with peace agreements signed at the highest levels of leadership, while others believe in grassroots movements and individual actions as a bottom-up approach.
What does the future hold for the conflict?
The future is uncertain, but maintaining the status quo and preventing further escalation are immediate priorities. Global interests and shifting public opinion may impact the dynamics of the conflict.
What is the international community doing to promote peace?
Many countries support the two-state solution, calling for an end to settlement expansion and serious investment in the Palestinian economy to reinforce the imperative of a durable peace.
Can a just and enduring solution be achieved?
While the road ahead may be difficult, a commitment to peace, coexistence, and human rights, along with the involvement of young voices and international support, offer hope for a better future.
Source Links
- https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2023/nov/03/a-two-state-solution-is-the-only-way-that-the-israel-palestine-problem-can-be-solved
- https://globalaffairs.org/commentary-and-analysis/blogs/pathways-peace-reflections-israeli-palestinian-conflict
- https://rpl.hds.harvard.edu/news/2023/10/30/rpl-news-biden-wants-two-state-solution-israeli-palestinian-peace-it-still-possible
Exploring the Two-State Solution: Pathway to Peace gaza strip conflict hamas aggression israeli-palestinian conflict isreal hamas war middle east conflict political unrest in palestine
Last modified: January 17, 2024