La Niña Persists for Rest of Winter, Experts Announce
Climate experts confirm La Niña persists for rest of winter, impacting weather patterns across the US. Stay informed on the latest La Niña forecast updates.

Federal climate experts confirm La Niña will last through winter. The forecast, led by NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center, shows ongoing ocean–atmosphere coupling in the tropical Pacific. This guides winter weather patterns across much of the United States.
The episode started in October, according to NOAA’s CPC. It remains active as winter arrives. CPC’s monthly update on Thursday, Dec. 11, confirms that La Niña will shape conditions from December through February.
Recent focus on the polar vortex has not changed the main story. Climate experts describe an “Arctic shuffle,” in which the vortex controls how much cold air descends southward. La Niña helps steer the storm track. Together, they influence winter weather patterns from the Pacific Northwest to the Southeast.
CPC guidance also notes that background conditions may persist into 2025–2026. This raises multi-season stakes for temperature and precipitation. Forecasters watch the Pacific for signs that the weather front will retain its grip into next year.
Key Takeaways
- NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center confirms La Niña will influence the rest of winter.
- Meteorological winter spans December to February, when impacts are most substantial.
- An “Arctic shuffle” links the polar vortex with storm-track steering.
- Climate experts expect continued background La Niña signals into 2025–2026.
- U.S. winter weather patterns will reflect both cold-air delivery and track guidance.
- The La Niña forecast highlights regional contrasts in temperature and precipitation.
Latest La Niña Weather Update from Climate Experts
Climate experts are watching the Pacific closely. They see calmer waters and a particular atmospheric pattern. This affects storms and temperatures in the U.S. It’s essential for planning in many areas.
Forecasters stress clarity over hype. They say the forecast gives us chances, not exact events. But the current setup helps narrow down what might happen.
NOAA CPC Confirms Ongoing La Niña Conditions
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center says La Niña is here to stay. They look at the ocean and how it affects the weather. This helps predict where cold air and storms will go.
Experts say the ocean and winds are working together. This means we can trust the forecast as winter goes on.
How the December Update Shapes the Winter Season Forecast
December is key for the winter forecast. It shows how the Pacific affects U.S. weather. The updates help predict storms and weather patterns.
This helps with weather planning. It tells us what to expect, whether it’s a short cold spell or a long one.
Difference Between Meteorological Winter and Calendar Winter
Meteorological winter is December to February. This is when forecasters base their predictions. The winter calendar is from late December to late March, but it’s not used for records.
This difference is essential for the La Niña forecast. The most substantial effects usually occur during meteorological winter. This makes it easier to compare years.
What “Persistence” Means for the La Niña Forecast
When forecasters talk about persistence, they mean the current weather pattern will likely stay. This means no sudden changes in la niña’s effects during the key months.
Persistence helps keep the forecast steady. It means we can rely on specific weather patterns and temperature chances.
La Niña Persists for Rest of Winter, Experts Announce
Forecasters at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center say La Niña persists for the rest of winter. They also say it will guide the jet stream. This means winter weather patterns will favor a more substantial, faster flow over the northern tier and a split, weaker branch farther south.
La Niña has been locked in place for months. This leads to familiar weather signals. The North often sees more storms, while the South can get drier at times.
These La Niña effects cause temperature swings. They push mild and cold pockets into new areas. The polar vortex also plays a role, bringing cold bursts into the Lower 48.
La Niña helps decide where these cold shots meet moisture. This is key for snowfall risk and regional precipitation in week-to-week winter weather patterns.
Even as experts announce a continued La Niña, forecasters note the pace can wobble. Sudden stratospheric warming or a stronger vortex may change the pattern for a spell. Regular updates keep pace with the evolving state, so that its effects remain clear as the season unfolds.
How La Niña and the Polar Vortex Steer Winter Weather Patterns
La Niña and the polar vortex work together to shape winter weather. It organizes the jet stream, while the polar vortex controls Arctic air. This teamwork decides where storms go and where they get cold.
The Arctic Shuffle: Cold Air Delivery vs. Storm Track Steering
The polar vortex brings cold air and guides storms. When the vortex wobbles, cold air rushes into the Plains and East. Tightening of the vortex brings milder weather, but clouds and snow stay in the North.
La Niña speeds up storm movement across the North. This leads to quick cold snaps and warm-ups. It’s a fast-paced weather rhythm.
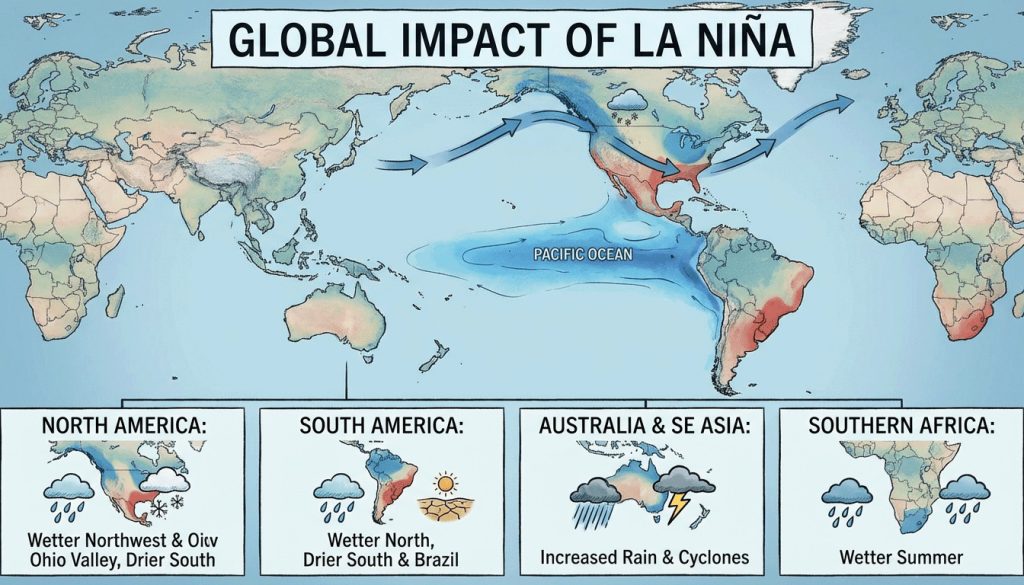
Regional La Niña Effects Across the United States
In the Pacific Northwest and northern Rockies, La Niña means wetter and stormier weather. The Great Lakes get lake-effect snow when it’s cold enough.
The Southwest and Gulf Coast tend to be drier. The South and East see warm-ups and cold snaps. La Niña influences these changes without setting a fixed pattern.
Temperature and Precipitation Signals: December–February Outlook
The Climate Prediction Center expects an active storm track in the North. This leads to snow chances near the Great Lakes. Energy and travel planners watch these periods closely.
Week to week, the weather can change quickly. This front suggests warmer weather in the South and variable cold in the East. The Northwest and Northern Plains are ready for cold snaps. Check out this polar vortex update for recent shifts.
La Niña Conditions and the 2025–2026 Implications
If La Niña continues, snowpack in the North and West might increase. Drought could spread in the South. River flows and soil moisture will also change as storms favor the North.
The Effects also impact the warm season. Forecasters will watch the equatorial Pacific to see if it persists or changes.
Other trending stories, on how your credit score really works. And how to increase your score.
Conclusion
Climate experts at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center say La Niña is key for winter. The December 11 update shows the impact on weather across the U.S., affecting the jet stream, storm paths, and temperature and rainfall patterns.
The “Arctic shuffle” describes this season’s weather setup. The polar vortex controls the extent of cold air while shaping where air and moisture meet. This leads to lake-effect snow near the Great Lakes, wetter areas in the North, and dry spots in the South.
Forecasters will update their predictions weekly. But for now, La Niña’s influence is evident. The CPC believes the effects could last into 2025–2026. This will impact water, drought, energy, and farming decisions.
For those following updates, experts offer a steady message. Expect ongoing forecasts that mix La Niña with the polar vortex. This will help plan for the winter season.
FAQ
What did NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center say in its latest La Niña weather update?
NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center (CPC) said La Niña is ongoing and will last through winter. They noted ocean cooling in the Pacific and an atmospheric response that drives the effects across North America.
How does the December CPC update shape the winter season forecast?
The December update sets the stage for winter, when the weather impacts are most substantial. It points to an active storm track, variable cold snaps, and regional weather patterns typical of this climate pattern.
What is the difference between meteorological winter and calendar winter?
Meteorological winter is the period from December to February, used for forecasting. The winter calendar is late December to late March. Forecasters focus on meteorological winter signals.
What does “persistence” mean in the La Niña forecast?
Persistence means it will continue to influence weather patterns. It means no quick change from your typical winter weather in the U.S. during the core months.
How are La Niña and the polar vortex interacting this season?
Experts talk about an “Arctic shuffle.” The polar vortex affects how Arctic air moves south. La Niña guides storm tracks and weather patterns, shaping where cold meets moisture.
Where are La Niña effects most noticeable across the United States?
La Niña makes the northern U.S. wetter and stormier. The southern U.S., like the Southwest and Gulf Coast, can be drier. But local weather can vary a lot.
What temperature and precipitation signals should people watch for December–February?
Expect more storms in the north and variable warmth in the South and East. The Northwest and Northern Plains might be cooler, with cold snaps depending on the polar vortex.
Will La Niña persist for the rest of winter, as experts announce?
Yes. CPC says La Niña will last through winter. It will shape weather patterns across the U.S., including temperature and precipitation.
How does the polar vortex affect cold air delivery under La Niña conditions?
The polar vortex controls how cold air moves south. When it weakens, cold snaps can be sharper. That influences where cold meets moisture, affecting snowfall.
What are the implications of the forecast for energy, transportation, and agriculture?
The forecast helps plan for heating demand, snow risks, and the effects of moisture on agriculture. It’s important for energy, transport, and early spring fieldwork.
How reliable are teleconnections in the United States?
Signals are most reliable in meteorological winter. While the signal is strong, week-to-week weather can change. It’s best to watch for updates on timing and intensity.
What is the outlook for La Niña into 2025–2026?
CPC expects La Niña to continue into 2025–2026. This could affect hydrology, snowpack, drought, and warm-season weather.
How does the “Arctic shuffle” influence snowfall?
The “Arctic shuffle” increases snow chances when cold and moisture align. Without this alignment, snowfall may be less, even in winter.
What should people in the southern tier expect during this La Niña?
The southern tier may see dry spells and variable warmth. Cold fronts can occur, but sustained wet periods are less common than in the north.
Why are experts stressing La Niña despite polar vortex headlines?
Experts focus on it because it sets the weather pattern. The polar vortex affects the delivery of cold air. It explains broader regional differences in weather.
How should the public interpret week-to-week swings during a persistent La Niña?
Swings are expected. The big picture is that short-term changes can occur. Regular updates help make near-term decisions.
Does La Niña increase the likelihood of lake-effect snow?
Yes, it can increase the likelihood of lake-effect snow. It favors colder air over the Great Lakes in an active storm track. Deeper cold from the polar vortex improves snow chances.
Where can people find official updates on the La Niña forecast?
Follow NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center for updates. The National Weather Service provides local forecasts and winter advisories. These sources offer the latest forecast and winter weather guidance.